
Meet The Specialist
We practice a minimally invasive approach to your foot or ankle problem with surgery as the last option.
Sprained ankles may occur when a person accidentally rolls, twists, or turns their ankle in an awkward way. When this occurs, ligaments in the ankle are being forced beyond their range of motion, thus causing an injury. Some symptoms that point to having a sprained ankle may include swelling, bruising, tenderness, and pain inflicted on the affected area. Some may also experience restricted range of motion or feel instability in the ankle.
There are many factors that play into the cause of ankle sprains. Simple, everyday activities like walking can lead to an ankle sprain if the activity is being done on an uneven surface. The same goes for running or exercising. Those who partake in sports may be more susceptible to obtaining a sprained ankle because they’re more likely to fall or land uncomfortably after a jump, which can lead to an injury.
It’s important to note that some of the main risk factors that can lead to sprained ankles are improper footwear, a prior ankle complication, weakness or lack of flexibility in the ankle region, and as mentioned above, uneven surfaces and involvement in sporting activities.






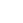
It's important to be evaluated by a doctor including x-rays because what you may think is just an ankle sprain may actually be an ankle fracture or foot fracture.
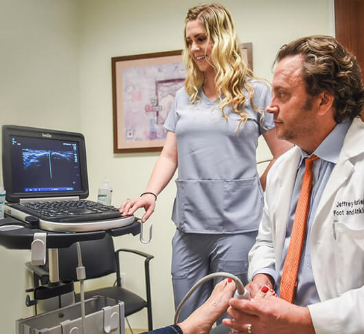
Meet The Specialist
We practice a minimally invasive approach to your foot or ankle problem with surgery as the last option.

Call now

Location
425 Haaland Dr. #201 Thousand Oaks, CA 91361
Timing
9:00 AM to 6:00 PM (Sat-Sun by appointment)
Why Urgent Care for Feet

We can treat 90% of cases seen in an emergency room for a fraction of the cost.
All of our doctors have on average 15+ year of experience specializing in foot and ankle care.
We provide on site x-ray that is designed specifically for foot and ankle. This will avoid re-taking an x-ray done improperly at an ER or standard Urgent Care.
Frequently Asked Questions
An ankle sprain is an injury to the ligaments in the ankle, typically caused by a sudden twist or impact. It results in pain, swelling, and limited range of motion, with varying severity depending on the ligament damage.
Symptoms of an ankle sprain include pain, swelling, bruising, difficulty bearing weight, limited range of motion, and possible instability, depending on the severity of the injury and ligament damage sustained.
An ankle sprain is diagnosed through a physical examination, during which a healthcare professional assesses pain, swelling, and range of motion. In some cases, imaging tests like X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Ankle sprain treatment typically involves the RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), pain-relief medications, and immobilization with a brace or wrap. In severe cases, physical therapy or surgery may be necessary for proper healing and recovery.
Ankle sprain healing time varies depending on the injury's severity. Mild sprains may heal in 1-3 weeks, while moderate sprains may take 3-6 weeks. Severe sprains can take several months to fully recover, possibly requiring physical therapy or surgery.
Ankle sprains can be partially prevented through proper footwear, balance and strength training, regular stretching, and taping or bracing the ankle during physical activity. Being cautious and avoiding uneven surfaces can also help reduce the risk of injury.
See a doctor for an ankle sprain if you experience severe pain, significant swelling, inability to bear weight, persistent instability, or if symptoms do not improve within a few days. A medical evaluation ensures appropriate treatment and recovery.
While exercising with an ankle sprain, focus on low-impact activities that don't strain the injured area, such as swimming or cycling. Avoid weight-bearing exercises until pain and swelling subside. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice on safe exercise.
Complications associated with ankle sprains include chronic ankle instability, persistent pain, re-injury, and the development of arthritis in the affected joint. Proper treatment and rehabilitation help reduce the risk of these complications.
Most sprained ankles do not require surgery. However, in severe cases with significant ligament damage or chronic ankle instability, surgery may be necessary to repair the injured ligament and restore normal function to the joint.

